| TL;DR: Most SaaS teams optimise for Google but lose visibility where buyers are now searching across generative engines. This case study breaks down the GEO framework we used to double AI referrals and increase Google AI Overviews by 315 percent. You will see the exact steps, the execution logic, and why these shifts created measurable impact. It’s a generative engine optimization case study by Concurate, the content agency for fintech saas marketing. |
Did you know traffic coming from AI tools converts three times better than traditional search?
When people ask ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini for help, they articulate their needs with far more clarity than they do in Google. Every business now wants to show up in those AI responses, specially for queries with higher buying intent.
Our client, a fast-growing B2B financing platform, wanted to move beyond adapting to this shift and actively lead it. Which raises a question – how do you get these LLMs to refer to your product or services?
Well, this case study breaks down how Concurate helped them drive a ~100% increase in AI-driven referrals through a targeted content strategy and tightly engineered blog assets.
| The Client A closing and financing platform for B2B subscriptions. It lets vendors offer flexible payment terms to their customers while still collecting the full contract value upfront. The platform embeds directly into existing sales workflows and includes AI-powered quoting, risk assessment, and collections. Backed by over $400M in capital, it helps SaaS businesses boost close rates, cash flow, and ARR without discounts or delays. |
The Challenge
When we first reviewed the client’s content performance, everything looked normal at a surface level. Traffic was steady, rankings were stable, and nothing in the Search Console hinted at a problem. But the story changed the moment we checked their presence on generative engines.
AI-driven referrals were almost flat.
Their blogs didn’t appear in AI Overviews.
And tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity weren’t pulling their content into answers at all.
That told us this clearly: the brand wasn’t discoverable in the places where SaaS buyers were now searching.
The deeper audit revealed why. Generative engines couldn’t confidently interpret the brand’s expertise because the entity signals across the web were scattered and weak. The content was built for traditional SEO, but modern AI systems need structured cues, expert identity, and consistent contextual signals to trust and cite a source.
So once we mapped these gaps, we built a dedicated generative engine optimization framework. Read on to this generative engine optimization case study to see what we did.
The Solution
To fix the client’s invisibility across generative search, we rebuilt their entire content foundation around one principle: generative engines reward content they can understand, trust, and retrieve without friction.
Here’s exactly how we made that possible:
#1 – Adding TL;DR Sections to Improve AI Interpretation
LLMs read the TL;DR to decide if they want to use your content as a reference or not in their responses. If there’s no quick summary, they ignore that piece of content.
To ensure that LLMs pick our content we wrote TL;DRs in this way:
- Open with the main pain point
- State the outcome clearly
- Mention the client naturally at the end
- Stay crisp: three to four sentences, max.
#2 – Adding Author Names and Expert Bios to Build Trust Signals
A CXL analysis of AI search shows that LLMs prefer citing content tied to verifiable experts rather than anonymous pages.
If the author is generic or invisible, the content gets deprioritized. So, here is how we reassigned every blog to authors with real credibility:
- Founders and product leaders for expert pieces
- The CMO for listicles and comparison guides
- Engineers or product contributors for technical deep-dives
#3 – Adding FAQ Schema to Make the Content Machine-Readable
LLMs extract clean Q&A blocks faster than long paragraphs, and pages with FAQ schema show up far more often in AI-generated answers. Without it, generative engines struggle to interpret your content.
So here’s how we added FAQ schema across the client’s blogs:
- Added a dedicated FAQ section at the end of each blog with new, high-intent questions not covered earlier.
- Generated consistent schema markup.
- Verified every schema block on validator.schema.org until it passed with zero errors or warnings.
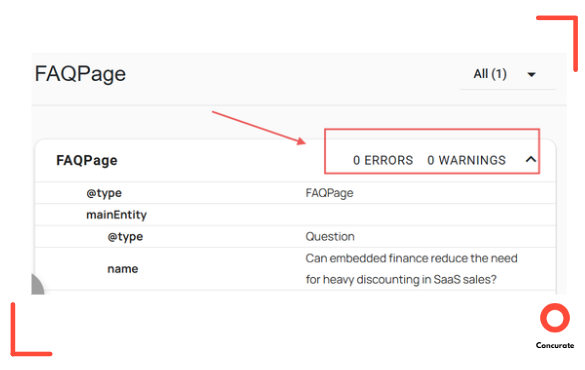
Source: validator.schema.org
- Published the text FAQs + schema together so LLMs could read both formats cleanly.
#4 – Acquiring Authoritative Backlinks to Strengthen Entity Confidence
In generative search, backlinks aren’t about SEO—they’re proof of legitimacy. LLMs rely heavily on earned media, high-DR directories, and third-party citations to decide whether your brand is a credible entity worth citing.
So here’s how we strengthened the client’s entity confidence through authoritative backlinks:
- Secured high-DR profiles on trusted platforms like TechCrunch (92), G2 (91), Opencart (91), Crunchbase (90), CB Insights (86).
- Added the brand to curated SaaS directories, market landscapes, and analyst-style listings LLMs regularly crawl.
- Published guest-authored articles on DR 70–90+ websites with natural brand mentions.
- Targeted niche SaaS, AI, FinTech, and B2B publications for contextual, category-aligned backlinks.
- Secured business citations on credible directories used in entity understanding.
- Built co-citation signals through LinkedIn thought leadership, webinars, and mentions.
#5 – Creating a Neutral, Well-Structured Wikipedia Page
LLMs treat Wikipedia as a primary reference source. If your brand doesn’t exist there, generative engines see you as an incomplete or low-confidence entity. Which directly reduces your chances of being cited.
So here’s how we built a credible, neutral Wikipedia presence for the client:
- Created a factual, non-promotional page outlining who the company is, what it does, and where it fits in the category.
- Used only reliable third-party sources (press, analyst mentions, independent reviews) to meet notability and neutrality standards.
- Added a complete infobox, structured sections (History, Funding, Activities, References), and proper internal/external links.
- Established an ongoing update process so the page remains active and trusted by generative engines.
#6 – Writing Q&A-Driven Blogs That Match Generative Query Patterns
Ahrefs’ AEO report shows that LLMs prefer pages where the question is the heading and the answer sits directly under it. If your content doesn’t follow this pattern, AI tools simply don’t pick it up.
So here’s how we structured Q&A blogs for the client to match generative query patterns:
- Identified every relevant buyer question using SEMrush, Ahrefs, PAA, and demo-call notes.
- Turned each heading into a direct user-style question.
- Wrote clear, concise answers and referenced the client’s product naturally where it fit.
- Ensured one question = one intent to avoid overlap.
- Interlinked Q&A blogs and added them to llms.txt for faster AI discovery.
#7 – Securing PR Placements That Act as High-Trust Evidence
These generative AI platforms are trained on a massive mix of editorial content, news articles, analyst reports, podcasts, and trusted newsletters — which means they inherit the credibility of those ecosystems.
So we focused on high-trust PR signals that AI engines already treat as credible:
- Founder commentary placed on Forbes to establish authoritative expertise.
- Product updates and releases featured on TechCrunch, Yahoo Finance, and similar outlets’ generative engines crawl heavily.
- Webinars and walkthroughs uploaded to YouTube to strengthen multimodal visibility.
There’s more to it: guest posts, podcasts, interviews, and other such efforts. They’re already in the pipeline (and we’re excited to roll them out).
#8 – Creating and Deploying an llms.txt File to Guide AI Crawlers
An llms.txt file gives AI crawlers a curated map of the content that actually represents your brand: definitions, product explainers, pricing breakdowns, FAQs, comparisons, and thought-leadership pages.
Instead of letting AI tools guess what matters, you explicitly tell them.
So we built a clear, curated llms.txt file that tells AI crawlers exactly what to read first:
- Listed all high-value, high-signal pages like product explainers, how-it-works content, FAQs, Q&A blogs, comparison pages, and category definitions.
- Structured the file exactly as laid out in our llms.txt creation guide to keep it clean and machine-interpretable.
- Added short contextual hints for each URL (“Product Overview,” “Core Definition,” “Primary FAQ”).
- Uploaded the file to the site’s root directory so generative engines can locate it automatically.
- Updated the file consistently as new strategic pages were published.
#9 – Publishing Consistently to Build a Strong Topical Footprint
If a brand publishes once in a while, AI models struggle to understand what the brand truly stands for. Consistency is what builds the topical graph that generative engines pull from.
So we made consistency a non-negotiable part of the strategy:
- Published four deeply researched, conversion-focused blogs every month — no fillers, no surface-level content.
- Chose topics based on trend analysis, buyer questions, and high-intent search patterns.
- Reviewed each piece through a strict editorial process and optimized it for generative engine interpretation.
- Interlinked every new blog into existing topical clusters and added it to the llms.txt file when relevant.
So… after all these efforts, we were eager to see the results.
Did they pay off?
Absolutely.
Let’s take a look.
If you prefer a quick walkthrough, we’ve also shared a short video version summarizing How We Drove a 100% Lift in AI Referrals and a 315% Surge in Google AI Overviews.
Results
After rolling out the complete generative engine optimization framework, the shift was almost immediate. Within just a few weeks, we started noticing a steady rise in how often the client’s content appeared across generative engines. And more importantly, how confidently these platforms were beginning to cite the brand.
The first clear signal came from the AI-driven referral data. Traffic coming specifically from AI platforms( like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and others) climbed by almost 100%.
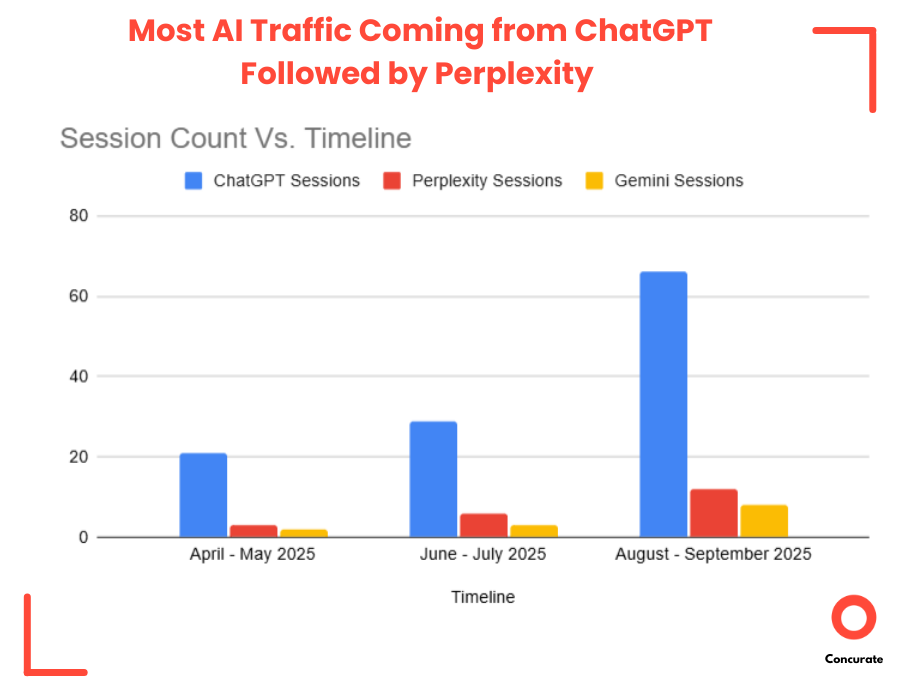
At the same time, Google’s own AI Overviews began picking up the client’s blogs more frequently. Check one example(as a proof) below:
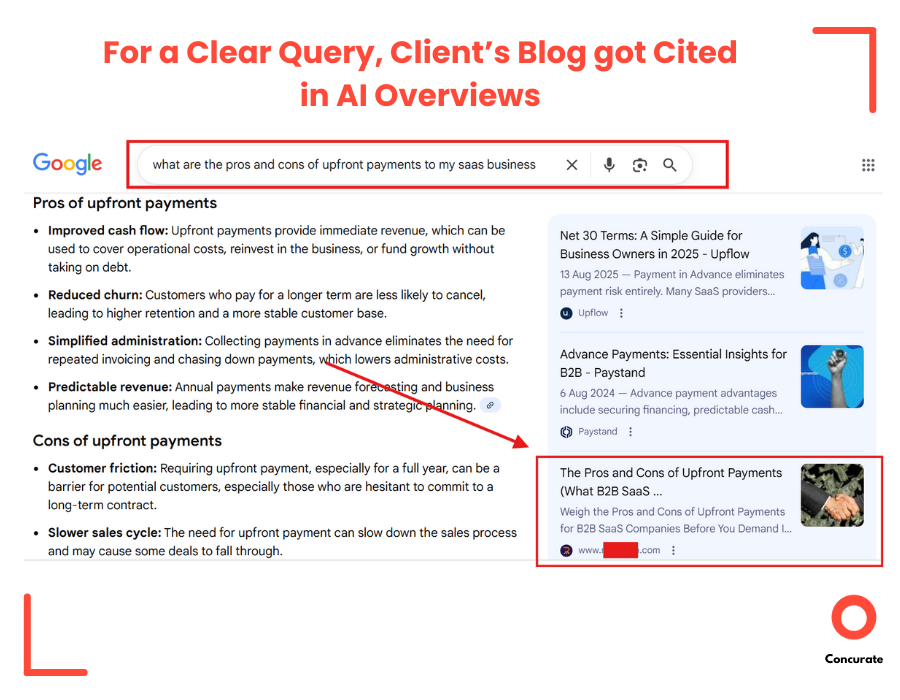
We saw a 315% increase in AI Overview appearances, especially for high-intent, product-adjacent topics where the client previously had zero presence.
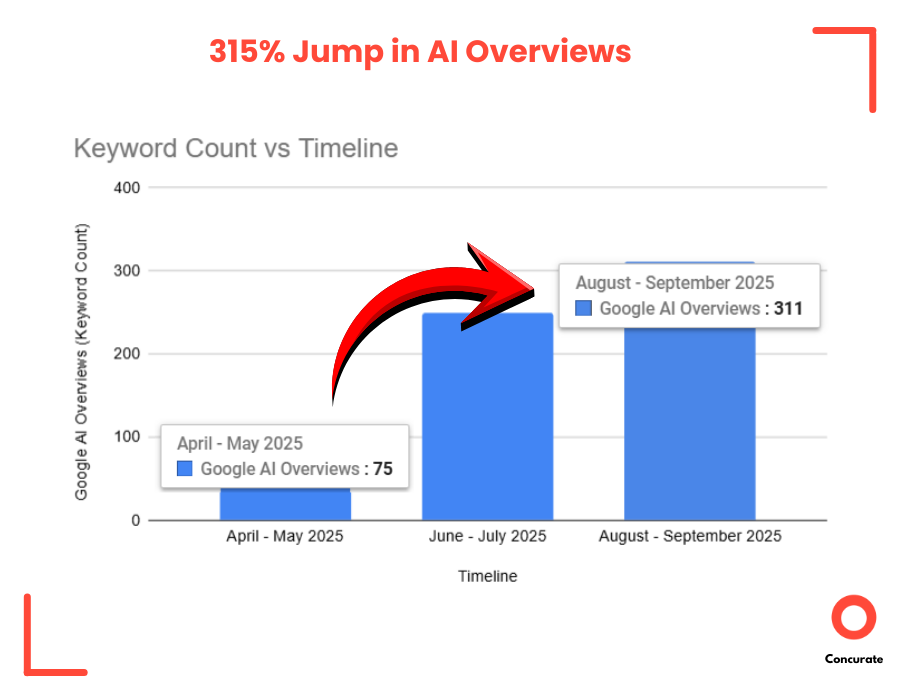
And here’s the interesting part: while we optimized heavily for generative engines, we didn’t lose any ground on traditional SEO. In fact, the opposite happened.
Additional Wins
Several of the blogs started showing up on the first page of Google and not just occasionally. Over time, when we calculated it was ~158.6% increase in published blogs reaching page 1 in 3 to 4 months. Many of them for competitive SaaS keywords. A few even captured SERP features, pushing the brand into both generative and classical search visibility at the same time.
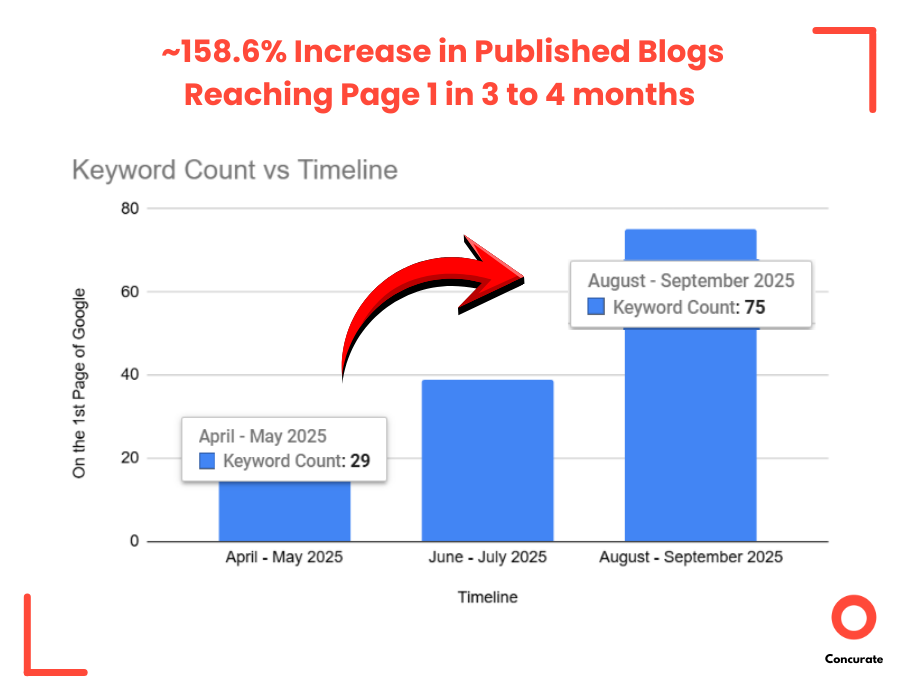
The impact wasn’t limited to rankings or citations either.
The real outcome showed up inside the sales pipeline.
Because every topic we created was tied to demo-call questions, category queries, and decision-stage information, the visibility gains translated directly into meaningful interest.
Over the next few months, the client recorded a 300% increase in qualified leads. And these weren’t casual visitors.
They were prospects evaluating category solutions, asking the right questions, and coming in with clear buying intent.
| On the 1st Page of Google | Google AI Overviews | AI Referrals | Leads | |
| April – May 2025 | 29 (Keywords) | 75(Keywords) | 43(Sessions) ChatGPT: 21 Perplexity: 3 Gemini: 2 | 1 |
| June – July 2025 | 39 (Keywords) | 250 (Keywords) | 69 (Sessions) ChatGPT: 29 Perplexity: 6 Gemini: 3 | 2 |
| August – September 2025 | 75(Keywords) | 311(Keywords) | 86(Sessions) ChatGPT: 66 Perplexity: 12 Gemini: 8 | 4 |
| %Change | ~158.6% Increase | ~314.67% Increase | 100% Increase | 300% Increase |
| Highlights -100% increase in AI-driven referrals -315% jump in AI Overviews -159% increase of published blogs reached Page 1 in 3 to 4 months -300% rise in high-quality leads |
Concurate – The Forward-Thinking Content Agency SaaS Brands Count On
At Concurate, we don’t wait for shifts to disrupt your pipeline. We adapt before they do.
When buyer search behaviour began moving from Google to generative engines, we moved with it. And this generative engine optimization case study is a solid proof of that.
When search patterns changed, we evolved our playbooks. That’s how we keep SaaS brands visible exactly where prospects now look — and trust.
And as a testament to the quality of work we deliver, right below you’ll find a screenshot from the client’s CMO appreciating the blog we created. Not because it looked good, but because it worked.
If you want the same kind of visibility lift our client witnessed — stronger AI citations, rising rankings, and a steady flow of qualified leads — partner with Concurate and sleep worry-free knowing your content engine is future-ready.

Book a discovery call with Concurate and let’s map the next chapter of your SaaS growth.
FAQs
1. How to Monitor Brand Visibility Across AI Search Channels?
The most effective way to monitor AI visibility is to set up a dedicated GA4 exploration that isolates traffic coming from AI tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, Copilot and others. You can filter Page Referrer using the right regex patterns, then break that segment down by landing page, device, country and conversions.
Our guide How to See If AI Tools Are Driving Traffic to Your SaaS Site already walks through this setup in detail.
Beyond GA4, you can also use AI visibility monitoring tools such as Ahrefs and Semrush. These platforms show how often your brand is cited across major AI engines, how frequently your domain appears in AI Overviews, and how your AI share of voice changes over time alongside traditional SEO metrics.
Together, these methods give you a reliable, end-to-end view of your brand’s visibility across the AI search ecosystem.
2. How to Rank in ChatGPT Search?
To “rank” in ChatGPT, you need to become the kind of source it trusts enough to cite.
That starts with your own site. Your product pages, about page, and case studies should clearly spell out what you do, who you serve, pricing model, and proof of results. LLMs lean heavily on that clarity when they assemble answers.
We did break this down here in detail: Where Does ChatGPT Get Its Information From For SaaS Recommendations?
The second lever is third party validation. ChatGPT overweights high authority and neutral sources review sites, comparison blogs, Wikipedia, and community discussions. If those places describe your product clearly and consistently, you show up more often and in a better light.
That is the core of “answer engine optimization,” which we covered in: Best Practices to Rank My Brand Higher in Answer Engines Like ChatGPT
The third lever is technical readiness for AI search. Clean site architecture, fast performance, structured data, and an llms.txt file all help AI crawlers understand what your pages are about and how to use them.
3. How to Optimize Content for Google AI Overviews?
Google AI Overviews behave more like a research assistant than a list of ten blue links. To appear there, you need to help it answer complex, multi part questions clearly.
First, target the right queries.
Long tail, problem centered questions work best, especially those that need explanation plus examples. Concurate’s guide on AI Overviews lays out this strategy and shows real prompts that consistently trigger Overviews.
Second, structure your page for “overview” style answers:
- Open with a clear, one paragraph answer to the core question
- Follow with scannable sections that break down steps, frameworks, and examples
- Use descriptive subheadings, bullet lists, and short sentences
- Add simple diagrams, tables, or checklists where they genuinely clarify the topic
Third, strengthen signals that your page is a safe answer for Google to amplify.
That includes accurate stats with sources, author expertise, internal links that build topical depth, and schema markup where relevant. Technical readiness matters too. Fast loading pages, mobile friendly layouts, and strong Core Web Vitals all support AI Overview inclusion.
4. What is the Difference Between GEO and SEO?
Here’s a simple table to make the GEO and SEO differences clear:
| Aspect | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
| Primary Goal | Rank on traditional search engine result pages | Be selected and cited inside AI-generated answers |
| How Users Search | Keywords typed into Google/Bing | Natural language questions asked to ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity |
| Output Format | 10 blue links, snippets, rankings | One synthesized answer with optional citations |
| What You Optimize For | Keywords, on-page SEO, backlinks, metadata, page speed | Entity clarity, structured explanations, llms.txt, consistency across third-party sources |
| Success Metric | Rankings, impressions, CTR, organic traffic | AI answer-share, citation frequency, AI-referred traffic |
| Content Style That Wins | Keyword-targeted pages with depth and relevance | Clean, structured explanations with steps, definitions and examples AI models can extract easily |
| Tools Commonly Used | Google Search Console, Semrush, Ahrefs, Screaming Frog | ChatGPT prompt testing, AI visibility tools, llms.txt validators, Semrush AI Visibility, Ahrefs BrandRadar |
| Where It Matters | Classic Google search | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, AI Overviews, Copilot, Claude |
| Relationship to Each Other | Long-standing foundation | Evolves on top of SEO to optimize for AI engines |